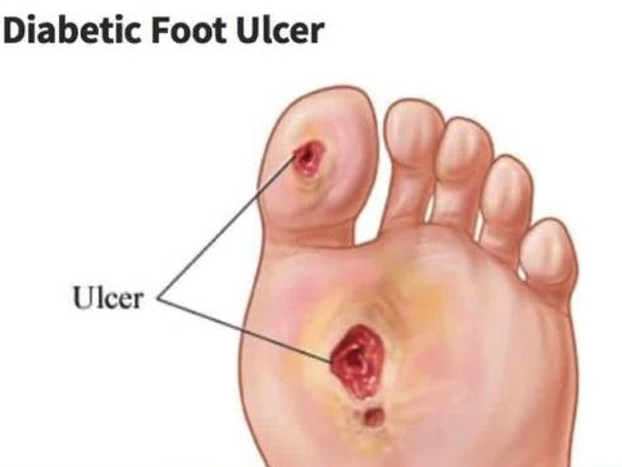
A diabetic foot ulcer can be redness over a bony area or an open sore. The ulcer can develop anywhere on your foot or toes. Ulcers usually develop on the bottom of the foot. You may not know you have an ulcer until you notice drainage on your sock. Drainage is fluid that may be yellow, brown, or red. The fluid may also contain pus or blood.
Risk factor for a diabetic foot ulcer?
Uncontrolled Blood sugar levels
Nerve damage and numbness in feet
A foot deformity, such as a bunion or hammertoe
Calluses or corns on your feet or toes
A decrease in vision that keeps you from seeing your feet clearly
Cigarette smoking or alcohol use
How is a diabetic foot ulcer diagnosed and treated?
Diabetic foot Specialist will ask about your symptoms and examine your foot and the ulcer. He or she may check your shoes. The goal of treatment is to start healing your foot ulcer as soon as possible. The risk for infection decreases with faster healing.
Prevent or treat an infection :
You may need to clean the ulcer and change the bandage daily. The bandage may contain medicines to help the ulcer heal. You may be asked to put medicine on your foot ulcer before you put on the bandage. The medicine may also prevent growth of tissue that is not healthy. If you have an infection, physician will give you antibiotics to treat it.
Dead tissue debridement :
The removal of dead skin and tissue around your foot ulcer can help with healing.
Manage blood sugar levels and other health problems :
blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels need to be controlled to help your foot ulcer heal.
Offload (take the pressure off) the foot ulcer :
You may need special shoes with insoles, cushions, or braces. You may be asked to use a wheelchair or crutches until your foot ulcer heals. These items will help keep pressure and irritation off the area of your foot ulcer. Your foot ulcer can heal faster without pressure and irritation.
Prevention of diabetic foot ulcers :
Good foot care may help prevent ulcers, or keep them from getting worse. The following can help you prevent diabetic foot ulcers :
Keep your blood sugar levels under control :
Healthy food choices and taking your medicines as directed may help control blood sugars. Contact your healthcare provider if your blood sugar levels are higher than directed.
Wash your feet each day with soap and warm water :
Do not use hot water, because this can injure your foot. Dry your feet gently with a towel after you wash them. Dry between and under your toes.
Apply lotion or a moisturizer on your dry feet :
Ask your physician what lotions are best to use. Do not put lotion or moisturizer between your toes. Moisture between your toes could lead to skin breakdown.
Check your feet each day :
Look at your whole foot, including the bottom, and between and under your toes. Check for wounds, corns, and calluses. Feel your feet by running your hands along the tops, bottoms, sides, and between your toes. Use a mirror to check your feet if you have trouble seeing the bottoms. Do not try to remove corns or calluses yourself. File or cut your toenails straight across.

Protect your feet :
Do not walk barefoot or wear your shoes without socks. Check your shoes for rocks or other objects that can hurt your feet. Wear cotton socks to help keep your feet dry. Wear socks without toe seams, or wear them with the seams inside out. Change your socks each day. Do not wear socks that are dirty or damp.
Wear shoes that fit well :
Wear shoes that do not rub against any area of your feet. Your shoes should be ½ to ¾ inch (1 to 2 centimeters) longer than your feet. Your shoes should also have extra space around the widest part of your feet. Walking or athletic shoes with laces or straps that adjust are best.
Do not smoke :
Nicotine can damage your blood vessels and increase your risk for foot ulcers.
Know the risks if you choose to drink alcohol :
Alcohol can cause high blood sugar levels and weight gain if you drink too much
Maintain a healthy weight :
A healthy weight can help you control your diabetes.